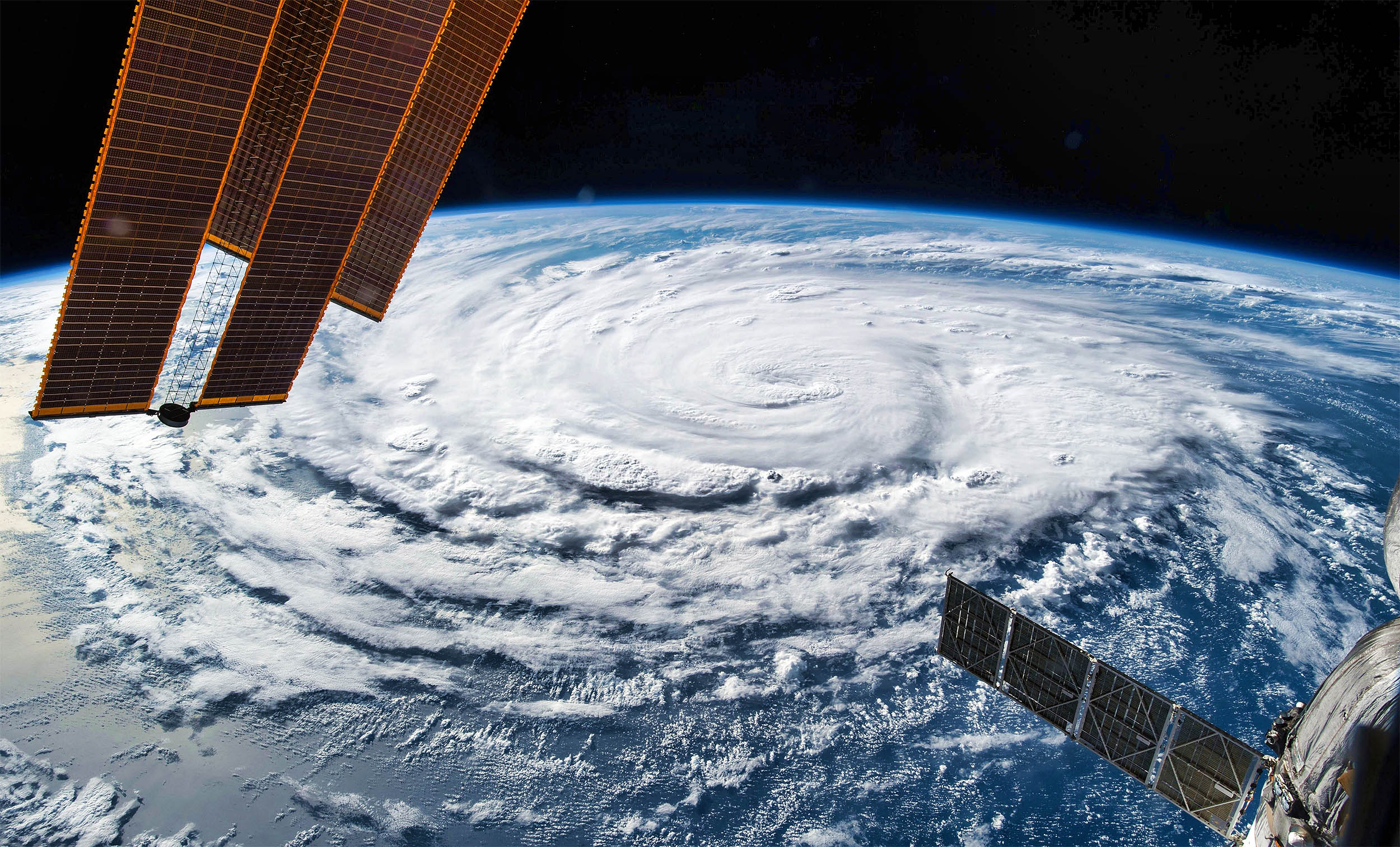
55 miles up, a never-before-seen event revealed by International Space Station sensors
Key Points:
- Hurricane Helene's impact extended beyond the Florida coast, as NASA's International Space Station detected previously unknown atmospheric waves about 55 miles above Earth, linking powerful storms to disturbances in the mesosphere.
- The Atmospheric Wave Instrument (AWE), installed on the ISS in 2023, captured ripple-like patterns in the upper atmosphere caused by the hurricane, revealing how surface weather events can affect air layers far above.
- These atmospheric waves can influence satellite operations by altering air density at high altitudes, potentially causing resistance that affects satellite orbits and communication systems.
- Advanced instruments like AWE and the Advanced Mesospheric Temperature Mapper (AMTM) provide new insights into the connection between Earth's surface weather and upper atmospheric changes, improving understanding