
New study reveals potential health risk behind tattoos
Key Points:
- A new study reveals that tattoo ink accumulates in lymph nodes, causing chronic inflammation, macrophage death, and altered immune responses, including changes in vaccine efficacy.
- Researchers observed that tattoo ink travels quickly from the skin to nearby lymph nodes and remains there for a lifetime, even after tattoo removal.
- The study found that tattooed mice showed a reduced response to the Covid-19 vaccine but an enhanced response to the UV-inactivated influenza vaccine, indicating varied impacts on immune function.
- This research is the first to explore how tattoo ink affects immunity, raising significant health concerns and highlighting the need for further studies to guide public health policies and ink safety regulations.
- Given the widespread popularity of tattoos globally, the findings emphasize the importance
Trending Business
A mom thought her daughter was texting friends before her suicide. It was an AI chatbot.
CBS News
TravelWits: Self-Book Luxury Hotels With Special Travel Agency Perks
One Mile at a Time
Rich People Staff Share Billionaire Secrets
BuzzFeed
How Reliable Are Rivians? Here's What Consumer Reports Says
Jalopnik
Woman wanted by FBI for allegedly defrauding Banc of California
ABC7 Los Angeles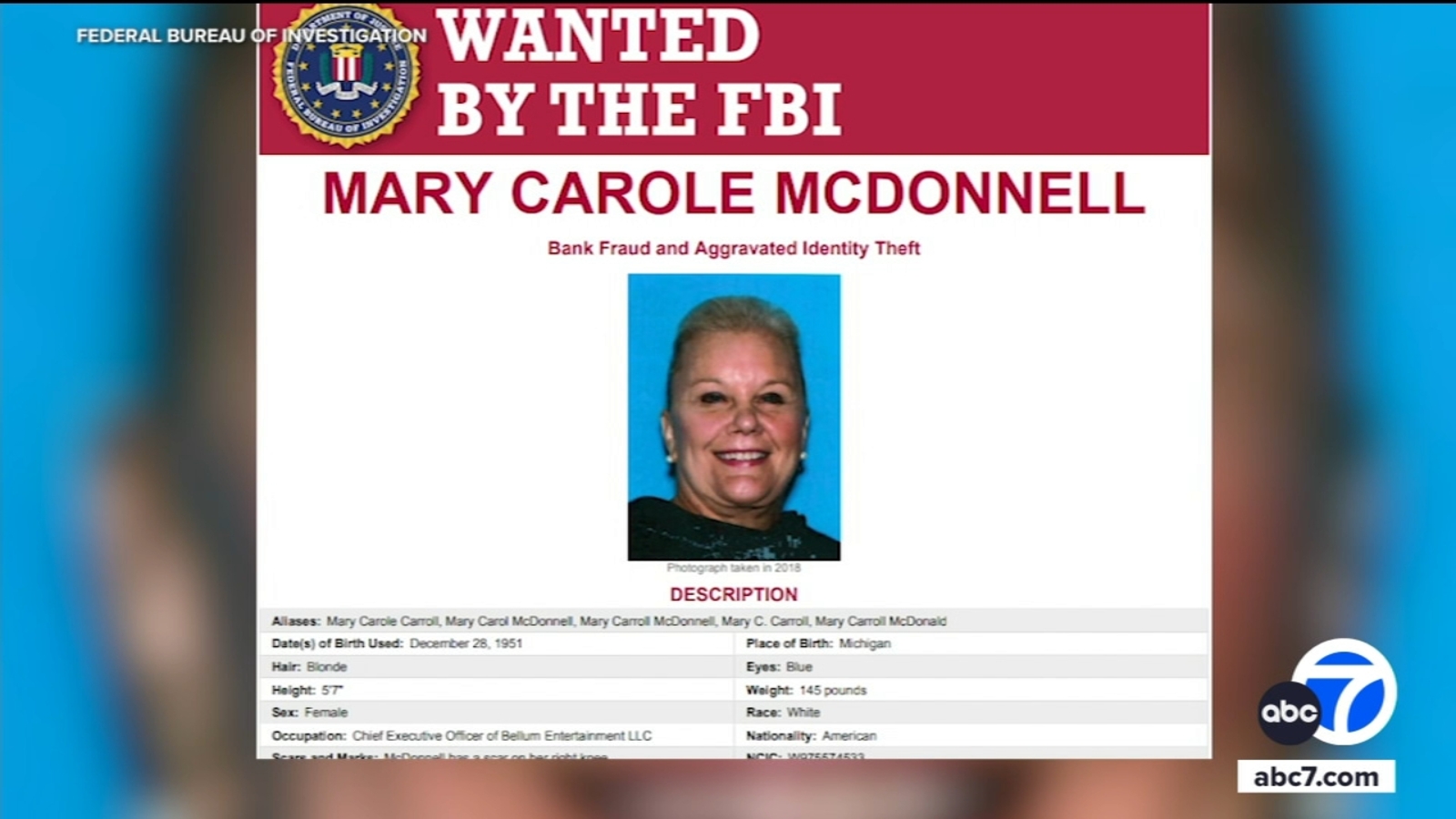
Trending Technology
USB Video Capture Devices: Wow! They’re All Bad!!
Hackaday
This Game Awards Teaser Just Keeps Getting More And More Puzzling
GameSpot
iam8bit sues Skybound Games for $4m, claiming breach of contract and theft of designs
Eurogamer
Gemini on Android Auto is the best place to use it yet
9to5Google
iPadOS 26.2 will fix my biggest gripe with Apple's current iPad software
9to5Mac
Trending Health
Hiker bit by coyote with rabies in New Mexico
KOB.com
‘Scromiting,’ a bizarre condition linked to chronic marijuana use, is on the rise
East Idaho News
What Does Nuclear Radiation Actually Do To Your Body?
bgr.com
University of Utah Health research funding reaches record $531M in 2025
KSL.com
Still Making Your Bed Every Morning? You Should Probably Stop… It's a Habit That Might Backfire
The Daily Galaxy